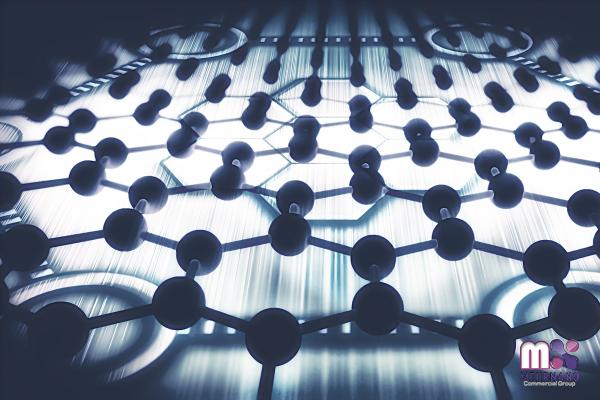
The field of nanomaterials has seen significant advancements in recent years, opening up new avenues for industries across the globe. These materials, characterized by their unique properties at the nanoscale, have the potential to revolutionize numerous sectors, such as electronics, medicine, energy, and manufacturing. In this article, we will explore four types of nanomaterials that hold immense promise in these diverse fields. 1. Graphene: Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice, is often referred to as a “wonder material.” With exceptional electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal properties, graphene has already found its way into electronic devices, batteries, sensors, and composites.
.
 Its high surface area-to-volume ratio and remarkable charge carrier mobility make it an ideal candidate for next-generation electronics and energy storage solutions. 2. Nanotubes: Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical carbon structures that possess excellent mechanical and electrical properties. They come in two main types: single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs). Thanks to their high aspect ratios and superior strength, CNTs are being explored for applications in lightweight materials, energy storage devices, and drug delivery systems. Their potential in strengthening composites, improving the efficiency of solar cells, and enhancing drug delivery mechanisms make them a notable nanomaterial. 3. Quantum Dots: Quantum dots (QDs) are nanoscale semiconductor particles that exhibit unique optical properties.
Its high surface area-to-volume ratio and remarkable charge carrier mobility make it an ideal candidate for next-generation electronics and energy storage solutions. 2. Nanotubes: Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical carbon structures that possess excellent mechanical and electrical properties. They come in two main types: single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs). Thanks to their high aspect ratios and superior strength, CNTs are being explored for applications in lightweight materials, energy storage devices, and drug delivery systems. Their potential in strengthening composites, improving the efficiency of solar cells, and enhancing drug delivery mechanisms make them a notable nanomaterial. 3. Quantum Dots: Quantum dots (QDs) are nanoscale semiconductor particles that exhibit unique optical properties.
..
 Due to quantum confinement effect, QDs possess size-tunable light emission properties that can be precisely tuned across the visible spectrum. This characteristic makes them highly attractive for applications in next-generation displays, solar cells, and biological imaging. With the ability to emit light efficiently and with customizable wavelengths, quantum dots hold great potential for revolutionizing the fields of lighting, energy, and healthcare. 4. Nanofibers: Nanofibers are ultrafine fibers with diameters on the nanoscale, typically ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers. These fibers can be produced from various materials, like polymers, metals, and carbon. Nanofibers’ large surface area and porosity make them suitable for applications such as filtration, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
Due to quantum confinement effect, QDs possess size-tunable light emission properties that can be precisely tuned across the visible spectrum. This characteristic makes them highly attractive for applications in next-generation displays, solar cells, and biological imaging. With the ability to emit light efficiently and with customizable wavelengths, quantum dots hold great potential for revolutionizing the fields of lighting, energy, and healthcare. 4. Nanofibers: Nanofibers are ultrafine fibers with diameters on the nanoscale, typically ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers. These fibers can be produced from various materials, like polymers, metals, and carbon. Nanofibers’ large surface area and porosity make them suitable for applications such as filtration, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
…
 Their potential to enhance air and water filtration systems, develop biocompatible scaffolds for tissue regeneration, and improve drug delivery precision makes them a crucial component of future technological advancements. Conclusion: The world of nanomaterials offers vast potential for innovation and disruption in multiple industries. Graphene, nanotubes, quantum dots, and nanofibers represent just a few of the many nanomaterials that are transforming various sectors. As research and development in this field continue to progress, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications that leverage the unique properties provided by nanomaterials. Harnessing these materials holds the key to technological advancements that will shape the future.
Their potential to enhance air and water filtration systems, develop biocompatible scaffolds for tissue regeneration, and improve drug delivery precision makes them a crucial component of future technological advancements. Conclusion: The world of nanomaterials offers vast potential for innovation and disruption in multiple industries. Graphene, nanotubes, quantum dots, and nanofibers represent just a few of the many nanomaterials that are transforming various sectors. As research and development in this field continue to progress, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications that leverage the unique properties provided by nanomaterials. Harnessing these materials holds the key to technological advancements that will shape the future.








Your comment submitted.