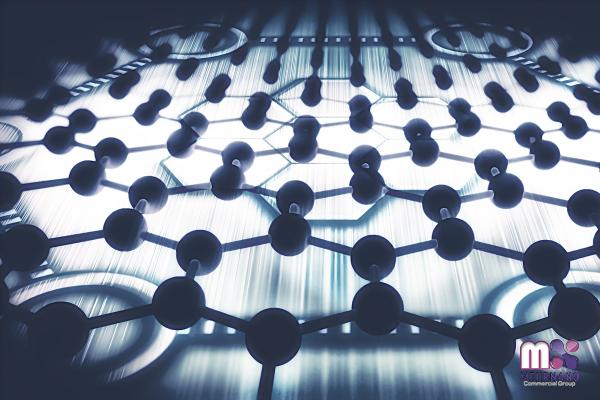
In recent years, there has been a surge of interest and investment in the field of nano materials due to their immense potential across various industries. At the heart of this revolution lies the intricate chemistry that underpins the creation and manipulation of nano materials. With unique properties and promising applications, understanding the chemistry of nano materials becomes crucial for businesses seeking to leverage these advancements. Nano Materials: A World of Opportunities: Nano materials refer to materials with dimensions typically less than 100 nanometers, where their physical and chemical properties significantly differ from bulk materials. These materials can be engineered at the atomic and molecular level, allowing for the tailoring of specific properties such as size, shape, surface chemistry, and composition.
.
 Characteristics and Benefits: The chemistry of nano materials enables a plethora of benefits that set them apart from conventional materials. Their increased surface area-to-volume ratio grants enhanced reactivity, catalytic efficiency, and mechanical properties. Additionally, nano materials possess exceptional thermal, optical, and electrical properties, rendering them indispensable in industries like electronics, energy storage, healthcare, and environmental remediation. Manufacturing Techniques: Understanding the chemistry behind manufacturing nano materials is pivotal. Techniques such as atomic layer deposition, sol-gel synthesis, chemical vapor deposition, and self-assembly are employed to precisely control size, shape, and composition. By altering the reactants, temperature, pressure, and reaction time, chemists can manipulate the synthesis process to yield custom nano materials catering to specific needs.
Characteristics and Benefits: The chemistry of nano materials enables a plethora of benefits that set them apart from conventional materials. Their increased surface area-to-volume ratio grants enhanced reactivity, catalytic efficiency, and mechanical properties. Additionally, nano materials possess exceptional thermal, optical, and electrical properties, rendering them indispensable in industries like electronics, energy storage, healthcare, and environmental remediation. Manufacturing Techniques: Understanding the chemistry behind manufacturing nano materials is pivotal. Techniques such as atomic layer deposition, sol-gel synthesis, chemical vapor deposition, and self-assembly are employed to precisely control size, shape, and composition. By altering the reactants, temperature, pressure, and reaction time, chemists can manipulate the synthesis process to yield custom nano materials catering to specific needs.
..
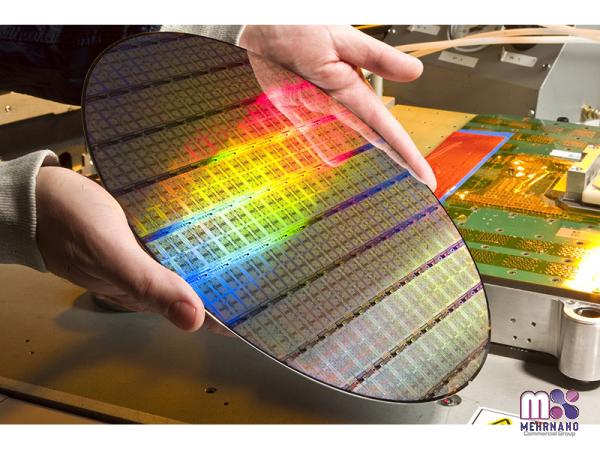
 Applications and Industries: The applications of nano materials span a wide range of industries, revolutionizing fields such as electronics, medicine, energy, and consumer products. In electronics, nano materials are paving the way for miniaturized devices with improved performance and energy efficiency. Biomedical applications include drug delivery systems, targeted therapies, and biomaterials for tissue engineering. The energy sector is exploring nano materials for advanced batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells, enhancing energy storage and conversion. Furthermore, nano materials are finding their way into consumer products like sensors, coatings, and textiles, improving functionalities and durability. Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Despite the immense opportunities, the widespread use of nano materials also raises concerns regarding their potential environmental and health impacts.
Applications and Industries: The applications of nano materials span a wide range of industries, revolutionizing fields such as electronics, medicine, energy, and consumer products. In electronics, nano materials are paving the way for miniaturized devices with improved performance and energy efficiency. Biomedical applications include drug delivery systems, targeted therapies, and biomaterials for tissue engineering. The energy sector is exploring nano materials for advanced batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells, enhancing energy storage and conversion. Furthermore, nano materials are finding their way into consumer products like sensors, coatings, and textiles, improving functionalities and durability. Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Despite the immense opportunities, the widespread use of nano materials also raises concerns regarding their potential environmental and health impacts.
…
 As such, ethical considerations play a vital role in the development and regulatory aspects of nano materials. Researchers and businesses need to address safety concerns, understand the behavior of nano materials in the environment, and ensure responsible production and disposal practices. Conclusion: As we delve deeper into the world of nano materials, the role of chemistry becomes increasingly crucial. The precise control and understanding of their chemical properties enable businesses to leverage their unique characteristics and unlock new possibilities. By embracing the nano revolution and staying attuned to the chemistry of nano materials, companies have the opportunity to drive innovation, create sustainable solutions, and disrupt industries, ultimately reshaping the future of technology and commerce.
As such, ethical considerations play a vital role in the development and regulatory aspects of nano materials. Researchers and businesses need to address safety concerns, understand the behavior of nano materials in the environment, and ensure responsible production and disposal practices. Conclusion: As we delve deeper into the world of nano materials, the role of chemistry becomes increasingly crucial. The precise control and understanding of their chemical properties enable businesses to leverage their unique characteristics and unlock new possibilities. By embracing the nano revolution and staying attuned to the chemistry of nano materials, companies have the opportunity to drive innovation, create sustainable solutions, and disrupt industries, ultimately reshaping the future of technology and commerce.








Your comment submitted.