In recent years, the demand for innovative and long-lasting surface coatings has witnessed a significant surge across various industries. One such breakthrough technology that has caught the attention of both professionals and consumers is nanoglass ceramic coating. This advanced coating offers outstanding durability, enhanced aesthetics, and superior protection against harsh elements, making it a game-changer in the field of surface protection. 1. Understanding Nanoglass Ceramic Coating: Nanoglass ceramic coating is a nanotechnology-based formulation that uses inorganic materials to create an ultra-thin protective layer on a surface. By harnessing the molecular properties of glass and ceramic, this coating provides exceptional hydrophobicity, chemical resistance, UV protection, and heat dispersion capabilities. Furthermore, its nanoscale thickness ensures that the original texture and color of the substrate are not compromised. 2. Key Applications: a. Automotive Industry: Nanoglass ceramic coating has gained immense popularity in the automotive industry due to its ability to protect vehicle exteriors from UV radiation, oxidation, water spotting, and scratches. Its hydrophobic properties also make it easier to clean and maintain the vehicle’s shine.
.
 b. Aerospace and Marine Industries: The harsh conditions faced by airplanes and ships necessitate superior protection against corrosion and weathering. Nanoglass ceramic coating offers excellent resistance to saltwater, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it an ideal choice for these industries. c. Architectural Sector: From glass windows to building facades, nanoglass ceramic coatings are being increasingly used to protect and enhance the aesthetics of architectural structures. The coating’s anti-graffiti properties and self-cleaning characteristics also make it a preferred choice in urban areas. d. Electronics and Appliances: Nanoglass ceramic coating is revolutionizing the electronics and appliance industry by providing an additional layer of protection against scratches, fingerprints, and dirt. This coating extends the lifespan of these products and improves their overall performance. 3. Advantages of Nanoglass Ceramic Coating: a. Longevity: Nanoglass ceramic coatings are designed to last significantly longer than traditional coatings.
b. Aerospace and Marine Industries: The harsh conditions faced by airplanes and ships necessitate superior protection against corrosion and weathering. Nanoglass ceramic coating offers excellent resistance to saltwater, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it an ideal choice for these industries. c. Architectural Sector: From glass windows to building facades, nanoglass ceramic coatings are being increasingly used to protect and enhance the aesthetics of architectural structures. The coating’s anti-graffiti properties and self-cleaning characteristics also make it a preferred choice in urban areas. d. Electronics and Appliances: Nanoglass ceramic coating is revolutionizing the electronics and appliance industry by providing an additional layer of protection against scratches, fingerprints, and dirt. This coating extends the lifespan of these products and improves their overall performance. 3. Advantages of Nanoglass Ceramic Coating: a. Longevity: Nanoglass ceramic coatings are designed to last significantly longer than traditional coatings.
..
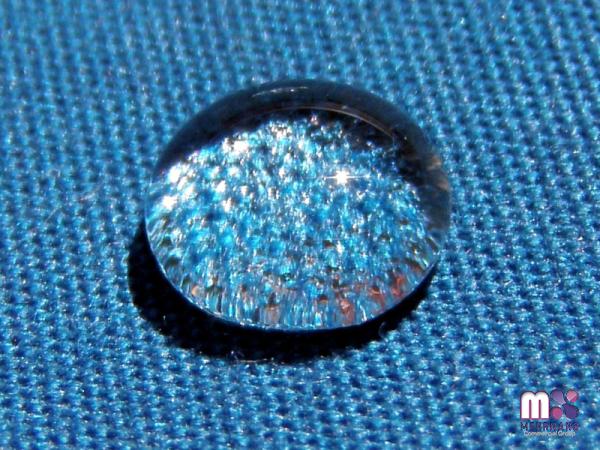
 With proper maintenance, they can offer protection for several years, reducing the need for frequent re-application. b. Enhanced Appearance: The coating’s optical clarity and self-leveling properties create a high-gloss finish that enhances the surface’s visual appeal. Nanoglass ceramic coatings are also available in a range of finishes, from glossy to matte, to suit various preferences. c. Easy Maintenance: The hydrophobic nature of nanoglass ceramic coatings minimizes the adherence of dirt, grime, and water spots on the surface. This makes cleaning effortless, reducing the time and effort required to maintain the coated surface. d. Environmental Sustainability: Nanoglass ceramic coatings are non-toxic and environmentally friendly. They do not release harmful chemicals or volatile organic compounds, making them a safe and sustainable option for coating surfaces. 4. Challenges and Future Prospects: While nanoglass ceramic coatings offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges.
With proper maintenance, they can offer protection for several years, reducing the need for frequent re-application. b. Enhanced Appearance: The coating’s optical clarity and self-leveling properties create a high-gloss finish that enhances the surface’s visual appeal. Nanoglass ceramic coatings are also available in a range of finishes, from glossy to matte, to suit various preferences. c. Easy Maintenance: The hydrophobic nature of nanoglass ceramic coatings minimizes the adherence of dirt, grime, and water spots on the surface. This makes cleaning effortless, reducing the time and effort required to maintain the coated surface. d. Environmental Sustainability: Nanoglass ceramic coatings are non-toxic and environmentally friendly. They do not release harmful chemicals or volatile organic compounds, making them a safe and sustainable option for coating surfaces. 4. Challenges and Future Prospects: While nanoglass ceramic coatings offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges.
…
 The high cost of the coating and the need for professional application are barriers that need to be addressed to make this technology more accessible to a wider market. However, ongoing technological advancements and research efforts are expected to improve coating durability, reduce costs, and streamline the application process in the near future. Conclusion: Nanoglass ceramic coating represents a groundbreaking advancement in surface protection. Its ability to provide exceptional durability, enhanced aesthetics, and superior resistance to various elements has positioned it as a preferred choice across several industries. As ongoing research continues to improve the technology and make it more accessible, nanoglass ceramic coating is set to revolutionize the way we protect and preserve surfaces, with far-reaching implications in automotive, aerospace, architecture, electronics, and other sectors.
The high cost of the coating and the need for professional application are barriers that need to be addressed to make this technology more accessible to a wider market. However, ongoing technological advancements and research efforts are expected to improve coating durability, reduce costs, and streamline the application process in the near future. Conclusion: Nanoglass ceramic coating represents a groundbreaking advancement in surface protection. Its ability to provide exceptional durability, enhanced aesthetics, and superior resistance to various elements has positioned it as a preferred choice across several industries. As ongoing research continues to improve the technology and make it more accessible, nanoglass ceramic coating is set to revolutionize the way we protect and preserve surfaces, with far-reaching implications in automotive, aerospace, architecture, electronics, and other sectors.








Your comment submitted.